United Reservoir North Cell Pump Station

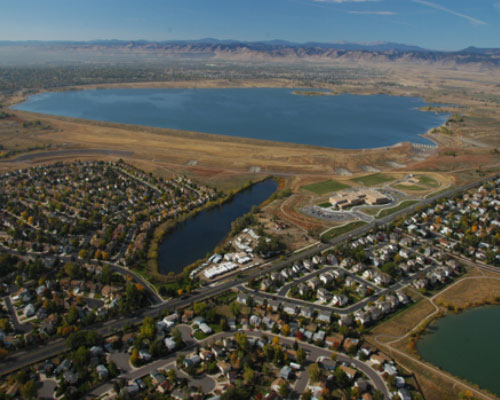
The United Reservoir North Cell Pump Station project consisted of replacing the existing system to accommodate the adjacent enlarged storage reservoir, to improve the functionality of the system, and to better manage excess sediments inherent to the river intake water. The pump station is used to divert flows from the South Platte River to Barr Lake and United’s North & South cells. The pump station is fed by or can return flow to the river via three large diameter pipes. The pump station consists of a connected two-celled wet well structure with a deep (64’) and a shallow (38’) rectangular (25’ x 11”) compartment. Both high and low head submersible pumps were installed in the wet wells along with discharge piping that allows for a variety of pumping scenarios up to a maximum rate of 50 cfs to Barr Lake. A gate is located between the two compartments to control hydraulic connectivity between the two wetwells depending on the specific pumping operation in use. Water is pumped to Barr Lake through a 36” ductile iron pipe. The system is automated and can be controlled remotely.
A schematic of the system is shown below along followed by a summary of the design components.
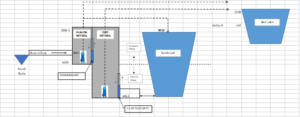
To help mitigate problems caused by disruption to the pumping operations and minimize downtime due to maintenance and cleaning of sediments and debris the following controls were included:
• Sediment/Debris basin positioned between the river intake pipes discharge and the shallow wet well. This basin can be accessed via a vac truck hose for solids removal.
• Removeable screens between the river intake pipes discharge and the pumps.
• Low head submersible pumps with a higher solids content threshold.
• Added redundancy with multiple pumps (four 12.5 cfs high head).
• Capability to pump to Barr Lake from either the shallow or deep wet well.
• Built in sprays used to keep silts suspended and prevent a buildup of solids in the shallow wet well.
• Flexibility to close river feed and pump directly from the North Cell if the sediment load from the river is high and there is enough water in the North Cell.

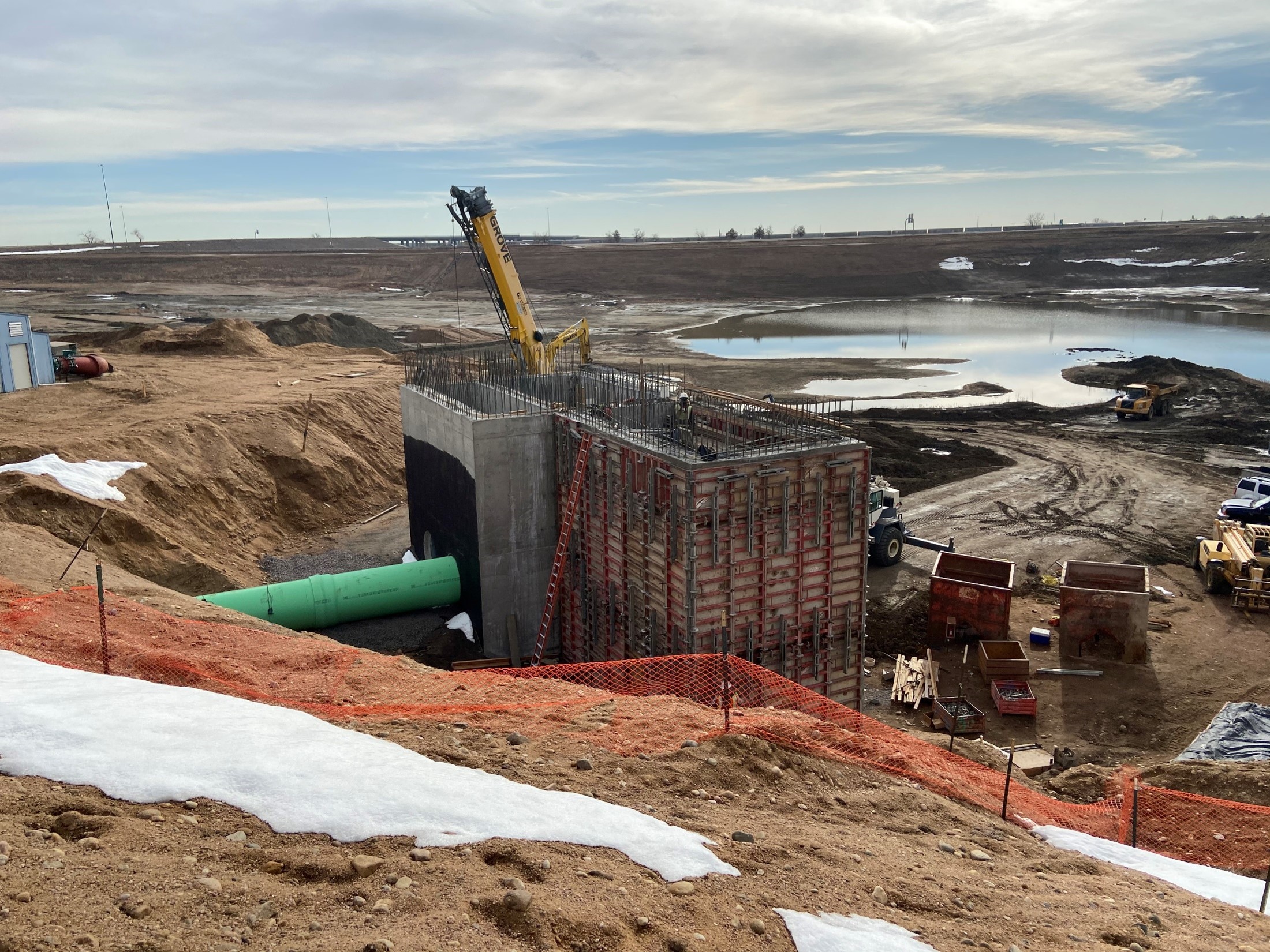
Concrete Wet wells under construction. Deep well~65′ deep; Shallow well ~35′ deep

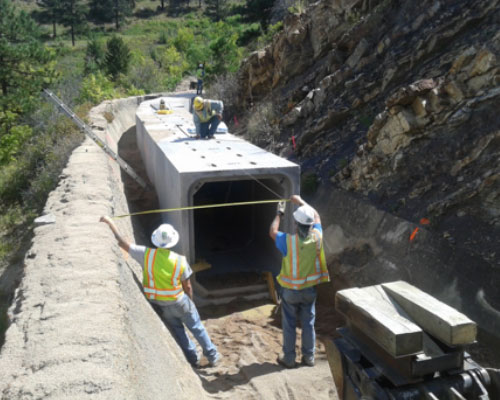
South River Intake Pipe Connection to Wet Well (Sediment Collection Bay)

Existing Ultraflow Pipe from River with Sliplined Hobas Pipe

Deteriorated Existing Ultraflow Pipe condition

Pump Discharge Header Shallow Well

Project Categories:
irrigation